Lines starting with ``('' are treated as part of the protocol.
All other lines are ignored and may be treated as comments. A request
has the following form:
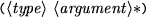
The following table lists the types of requests and their meaning.
Some types are vital and have to be understood by every
implementation, while other types provide information about the
internal state of the optimizer and can be safely ignored by the
framework.
- evaluate
- (required)
(evaluate ({( variable name
variable name
 value
value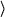 )}
)} )
((id
)
((id 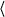 request id
request id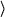 )))
)))
Requests an evaluation. The request id is a positive integer.
- gradient
- (required)
(gradient ({(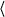 variable name
variable name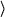
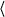 value
value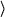 )}
)} )
((id
)
((id 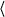 request id
request id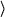 )))
)))
Requests an evaluation for the calculation of an gradient. Apart
from giving the reason why the optimizer sends this request, there
is no semantic difference to evaluate.
- result
- (required)
(result 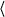 status
status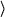 {(
{(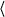 variable name
variable name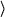
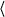 value
value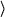 )}
)} )
)
Returns the result of an optimization. The status, an integer
value, indicates if the optimization was finished successfully. The
meaning of the status code depends on the optimizer used.
- jacobian
- (optional, informative)
(jacobian 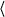 rest
rest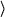 )
)
The entries of the Jacobian, provided by some optimizers. For
debugging purposes only.
- reduction
- (optional, informative)
(reduction 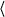 value
value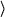 )
)
Information provided by some optimizers, cf. [92].
- statistics
- (optional, informative)
(statistics 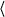 rest
rest )
)
Information provided by some optimizers, cf. [92].
Clemens Heitzinger
2003-05-08
