3.2 Mesh Adaptation Algorithms
A mesh adaptation algorithm takes a multi-region mesh
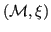 as the input to create a resulting mesh
as the input to create a resulting mesh
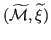 , for which the underlying space of all regions is the same:
, for which the underlying space of all regions is the same:
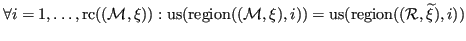 .
In other words, the input mesh and the resulting mesh conform to the same geometry.
.
In other words, the input mesh and the resulting mesh conform to the same geometry.
Mesh adaptation algorithms can roughly be split into three groups, those being topological operations (cf. Section 3.2.1), geometrical operations (cf. Section 3.2.2), and mixed operations (cf. Section 3.2.3). These operations are often used for mesh improvement, as discussed in Section 3.2.4. At last, Section 3.2.5 gives an overview of a selection of mesh adaptation software tools.
Subsections
florian
2016-11-21