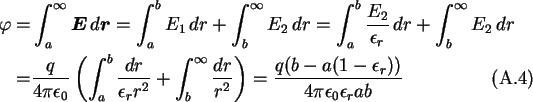


Next: A.3 Capacitance of Two
Up: A Capacitance Calculations
Previous: A.1 Self Capacitance of
A.2 Self Capacitance of a Sphere with a Dielectric Shell
Figure A.1:
Conducting sphere with dielectric shell.
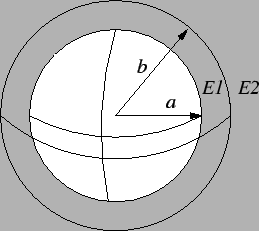 |
The capacitance of a conducting sphere with a dielectric shell, as shown
in Fig. A.1, is calculated using the boundary condition
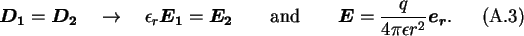
The potential of the sphere is calculated by a path integral from the
surface of the sphere to infinity over the electric field.
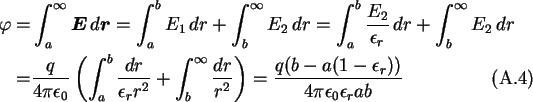
And hence the capacitance of a conducting sphere with a dielectric shell is

Christoph Wasshuber