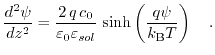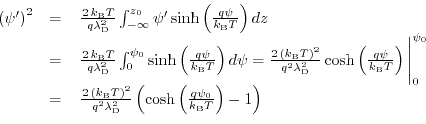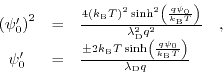


Next: D. Relation Between Charge
Up: Appendix
Previous: B. Expressing the Equations
C. Estimating the Total Charge in the Diffusive Layer
The Poisson-Boltzmann equation can be solved for the total charge in the diffusive layer in a similar manner the way it is done for the semiconductor surface potential. Beginning with (5.13):
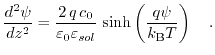 |
(7.21) |
Reexpressing it via the Debye length,
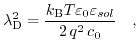 |
(7.22) |
leads to the following expression:
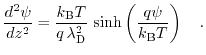 |
(7.23) |
This equation can be rewritten by applying the following identity:
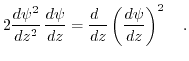 |
(7.24) |
Substituting (7.24) into (7.23) leads to a first order differential euqation:
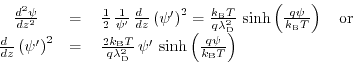 |
(7.25) |
(7.25) can be solved via separation of variables. Under the condition of a vanishing electric field for
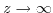 the following solution can be derived:
the following solution can be derived:
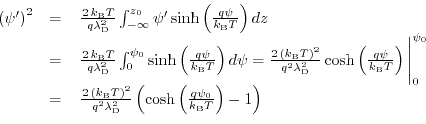 |
(7.26) |
Exploiting the identity
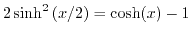 , the expression for
, the expression for
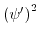 can be formulated as:
can be formulated as:
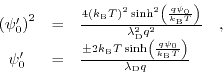 |
(7.27) |
In the last calculation step Gauß's law is utilized to express the total charge per unit area in the Gouy-Chapman layer:
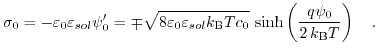 |
(7.28) |



Next: D. Relation Between Charge
Up: Appendix
Previous: B. Expressing the Equations
T. Windbacher: Engineering Gate Stacks for Field-Effect Transistors