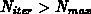 .
.
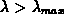 . In this case, the algorithm is failing to
move forward even though the method of steepest descent is used
. In this case, the algorithm is failing to
move forward even though the method of steepest descent is used .
.
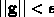 .
.





The iterations are continued until convergence which is denoted by either a small relative change in the sum of squares error (F), or by a small change in each parameter value relative to the previous iteration values. Other termination criteria are indicative of error conditions that occur when the optimization problem is ill posed such as when:
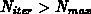 .
.
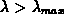 . In this case, the algorithm is failing to
move forward even though the method of steepest descent is used
. In this case, the algorithm is failing to
move forward even though the method of steepest descent is used .
.
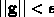 .
.
As in other optimization problems, the convergence to a solution does not guarantee that the global minimum of F has been reached.