


Next: 5.1.5 Results
Up: 5.1 Optimization with a
Previous: 5.1.3 Simulation Flow of
The time for the simulation of the process flow and the electric
characterization takes about 40 minutes, so a direct optimization
is not suitable to solve this problem.
But the problem can be solved using Design of Experiments and Response Surface Methodology.
This is done by the generation of an experimental design,
simulation of the design points, fit of a response surface, and, finally, optimization
using the data from this fitted surface (see Figure 5.2).
Figure 5.2:
Main steps for solving the optimization problem.
|
![\includegraphics[width=.8\linewidth]{graphics/appa_optimize.eps}](img224.gif)
|
In the simulation framework a complex optimization task consists of
several analysis functions.
Figure 5.3 shows the task using DoE, RSM, and optimization
steps. The numbers in the figure indicate the actions which have to be
done by the framework listed below.
Figure 5.3:
Structure of the optimization task using DoE and RSM.
|
![\includegraphics[width=\linewidth]{graphics/appa_task.eps}](img225.gif)
|
- 1.
The framework reads the specification of the analysis task from the file. It
consists of the reference of the stored simulation flow, the
definition of control and response parameters with their location in
the flow, and additional information like default values and ranges.
The sequence of analysis steps (from step 2-9) is also read from this
file.
- 2.
The input for the DoE module (ranges of the control
variables and the specified design) and start the DoE program is
prepared.
- 3.
After termination of the program the framework collects the evaluated
result of the DoE module and adds the control parameter values of
the new experiments to the experiment table.
- 4.
The set of controls from the referenced process flow and the
experiment table are used to generate the experiments. An
experiment consists of the simulation of a process flow and
extraction of the results.
- 5.
The experiments are simulated
using the integrated simulators and tools. The responses where
extracted from simulation output.
- 6.
All responses are collected from the finished runs and added to
the experiment table.
- 7.
After all experiments have been carried out, the complete data
of the experiment table are given to the Response Surface Methodology module for
evaluation.
- 8.
The ranges, start values and target functions are passed to the
optimizer.
- 9.
The optimizer requests evaluations from the RSM module and
receives the calculated target function until an optimum is found.
The output values of the device simulation used for the
performance qualification
are the on-resistance RDS on
and the breakdown voltage UD b.
Two parameters of the process flow are chosen to improve these
properties; the epitaxial doping value nepi and the thickness of
the epi-layer depi.
The goal of this optimization is to minimize the on-resistance while
keeping the breakdown voltage above 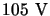 .
.



Next: 5.1.5 Results
Up: 5.1 Optimization with a
Previous: 5.1.3 Simulation Flow of
R. Plasun
![\includegraphics[width=.8\linewidth]{graphics/appa_optimize.eps}](img224.gif)
![]() .
.