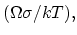 |
(216) |
Interconnect reliability due to thermal effects is becoming a serious design issue particularly for dense packed interconnect structures. Thermal effects are inseparable aspects of electrical power distribution and signal transmission through the interconnects due to self-heating caused by the flow of current. Thermal expansion mismatch between the metal and the passivation layer causes stress which leads to fatigue and failure of the metalization [2]. The first problem to be modeled is self-heating due to an electrical current, which is described by the following equations [76],
In each electromigration model discussed below, the effect of electromigration is proportional to current density. Most of the available TCAD electromigration reliability tools [65,68] are exclusively based on current density simulation.
One of the well established results is that the current density exponent ![]() in Black's equation is caused by significant Joule self-heating at high current densities [7].
in Black's equation is caused by significant Joule self-heating at high current densities [7].