


Next: 8 Solving Procedure
Up: 5 Void evolution and
Previous: 6 Maintaining the Grid
7 Grid Adaptation
The grid adaption algorithm used in this work is a version of
the algorithm introduced in [89] and consists of a grid
refinement algorithm and a grid coarsening algorithm.
The refinement algorithm is based on recursive bisecting of
triangles. A triangle is marked for refinement if it complies with
some specific refinement criterion 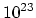 . In our application we used
. In our application we used
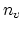 for the initial refinement and
for the initial refinement and 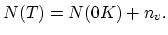 for the grid
maintaining refinement. For every
triangle of the grid, the longest one of its edges is marked
as refinement edge.
The element and its neighbor element which also contains the same refinement edge are refined by bisecting this
edge (Fig. 4.6). We can define refinement of the element in
the following way:
for the grid
maintaining refinement. For every
triangle of the grid, the longest one of its edges is marked
as refinement edge.
The element and its neighbor element which also contains the same refinement edge are refined by bisecting this
edge (Fig. 4.6). We can define refinement of the element in
the following way:
Now, the overall refinement algorithm can be formulated as follows:
The parameter max_refinement_depth limits the number of
bisecting of a triangle.
The grid is refined until there is no more element marked for refinement or the maximal refinement
depth is reached.
The coarsening algorithm is more or less the inverse of the refinement
algorithm. Each element that does not fullfil criterion 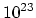 is
marked for coarsening. The basic idea is to find the father element whose refinement
produced the element in consideration.
The following routine coarsens as many elements as possible, even more
than once if allowed:
The complete adaption of the grid is reached by sequential invoking
of the
grid refinement and of the grid coarsening algorithm.
is
marked for coarsening. The basic idea is to find the father element whose refinement
produced the element in consideration.
The following routine coarsens as many elements as possible, even more
than once if allowed:
The complete adaption of the grid is reached by sequential invoking
of the
grid refinement and of the grid coarsening algorithm.



Next: 8 Solving Procedure
Up: 5 Void evolution and
Previous: 6 Maintaining the Grid
J. Cervenka: Three-Dimensional Mesh Generation for Device and Process Simulation
![]() . In our application we used
. In our application we used
![]() for the initial refinement and
for the initial refinement and ![]() for the grid
maintaining refinement. For every
triangle of the grid, the longest one of its edges is marked
as refinement edge.
The element and its neighbor element which also contains the same refinement edge are refined by bisecting this
edge (Fig. 4.6). We can define refinement of the element in
the following way:
for the grid
maintaining refinement. For every
triangle of the grid, the longest one of its edges is marked
as refinement edge.
The element and its neighbor element which also contains the same refinement edge are refined by bisecting this
edge (Fig. 4.6). We can define refinement of the element in
the following way:
![\fbox{\parbox[b][6.9\baselineskip][s]
{\boxwidth}{ \textbf{Algorithm 1.} \texti...
...\hspace*{0.25cm}bisect(element)
\ \hspace*{0.25cm}bisect(neighbor)
\ \}
}}}}](img928.png)
![\fbox{\parbox[b][11.7\baselineskip][s]
{\boxwidth}{ \textbf{Algorithm 2.} \text...
...} \hspace*{0.25cm}recursive\_refine(element)
\ \hspace*{0.25cm} \}
\ \}
}}}}](img929.png)
![\fbox{\parbox[b][6.6\baselineskip][s]
{\boxwidth}{ \textbf{Algorithm 3.} \texti...
...se the element\_father
\ \hspace*{0.25cm}coarse the father\_neighbor
\ \}
}}}}](img930.png)
![\fbox{\parbox[b][11.3\baselineskip][s]
{\boxwidth}{ \textbf{Algorithm 4.} \text...
...ment)
\ \hspace*{0.25cm} \} until do\_coarsen\_once\_more is false
\ \}
}}}}](img931.png)