

 Previous: 2.1.1 The Boltzmann Equation
Up: 2.1 The Boltzmann Poisson
Next: 2.1.3 Dimensional Reduction
Previous: 2.1.1 The Boltzmann Equation
Up: 2.1 The Boltzmann Poisson
Next: 2.1.3 Dimensional Reduction
By definition the potential 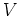 fulfills
fulfills
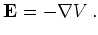 |
(2.7) |
By Maxwell's equations we have
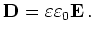 |
(2.8) |
and
Here
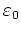 is the electrical permittivity of free
space and
the dimensionless dielectric constant
is the electrical permittivity of free
space and
the dimensionless dielectric constant
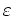 is a material
dependent parameter.
In our case the charge density
is a material
dependent parameter.
In our case the charge density 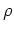 is given by
is given by
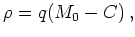 |
(2.10) |
with 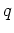 the (negative) elementary charge,
the (negative) elementary charge, 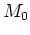 the
zeroth moment, that is, the particle density, and
the
zeroth moment, that is, the particle density, and 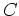 the net doping.
the net doping.


 Previous: 2.1.1 The Boltzmann Equation
Up: 2.1 The Boltzmann Poisson
Next: 2.1.3 Dimensional Reduction
Previous: 2.1.1 The Boltzmann Equation
Up: 2.1 The Boltzmann Poisson
Next: 2.1.3 Dimensional Reduction
R. Kosik: Numerical Challenges on the Road to NanoTCAD
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Previous: 2.1.1 The Boltzmann Equation
Up: 2.1 The Boltzmann Poisson
Next: 2.1.3 Dimensional Reduction
Previous: 2.1.1 The Boltzmann Equation
Up: 2.1 The Boltzmann Poisson
Next: 2.1.3 Dimensional Reduction