Footnotes
- ...
- The view on ECAD
is greatly simplified, there is no layout generation
and extraction, no back-annotation, and no schematic level shown in
Figure 1.1, which entirely focuses on TCAD aspects and its
interface to ECAD. For a discussion of ECAD methodology, see, e.g.,
[3] and [2].
- ...
- A good review and classification of ECAD
systems is given in [2]
- ...
- Currently in use at 7 institutions in Europe, Japan, and USA
- ...
- When in doubt, I have chosen the most
popular name instead of, e.g., that of a newly created system
component, to denote a TCAD system
- ...
- derivative of SUPREM-4 file format
- ...
- derivative of SUPREM-4 file format
- ...
- described in detail in Chapter 4
- ...
- described in detail in Chapter 3
- ...
- Interesting remarks on the technology dependence of
TCAD methodology can be found, e.g., in [14].
- ...
- See also
Section 8.5
- ...
- This
difference in focus often leads to severe misunderstanding.
- ...
- this topic is picked up
again in Section 8.
- ...
- Although problem formulation does not require
an implementation at all, the common terms and nomenclature
implicitly (or explicitly) defined by a data level implementation
can facilitate the problem definition effort significantly by
providing a common conceptual basis.
- ...
- See also Section 8.5
- ...
- Note that the
framework engineer has to cope with the
sometimes conflicting needs of users, tool integrators, and tool
developers.
- ...
- This is of course not true for distinct modules within
the TCAD system, which solve clearly defined problems and a top-down
design can be successfully applied. (See, e.g. Section 6.2.)
- ...Portability.
- The base system integration,
as described in Section 2.5, fosters portability.
- ...Level.
- As the TCAD data level is not subject of this
text, the reader is referred to [44] for a detailed
discussion data level aspects.
- ...
- These services are not a must for an
application-framework. A serious TCAD system, however, can not do
without them. The generic services
may also be provided in form of applications, which is merely
an implementation detail. From a conceptual point of view, they
may still be considered part of the TCAD framework.
- ...
- This decomposition is not
without overlap.
- ...
- VMAKE
will be part of another text.
- ...
- Note the re-use and conceptual integrity of
this choice.
- ...
- VISTA's data level
will be subject of another text, a detailed description can be found in,
e.g., [44].
- ...are:
- Standard materialtypes are technology-dependent
and are managed by the VISTA material server.
- ...
- These conventions are in addition to the
rules and restrictions which are already
enforced by the PAI.
- ...
- For example, within the past five years, four entirely
different window systems have been in use on Digital Equipment's
Workstations (VWS, DecWindows, Motif, Windows NT)
- ...
- See Section 8.6.1.
- ...
- The motivation for a dedicated task level was
given in Section 2.1.
- ...
- The importance of the aforementioned requirements
for tool integration and tool control (Section 4.1),
as well as the need
to connect the applications to the interpreter with
appropriate and feasible
mechanisms can easily be recognized.
- ...
- For an explanation, see, e.g., [85]
- ...
- February 1994
- ...
- The term simplex
is used for several other purposes; it is not intended to clarify
the meaning of the term as such or its relationship
to other fields.
- ...
- An allocation size of
8 entities is assumed for every simplex block in Figure 5.2
- ...
- Ray-casting
follows the ray against its propagation direction from the observer
to the point of origin.
- ...
- For reproduction purposes, the
color image had to be mapped to grey-scale. Comprehension of
the figure is facilitated by interpreting it as X-ray image.
- ...
- For the sake of comprehensibility, the
definition is slightly inexact
- ...
- All subsequent
statements and considerations
do not make use of the orientation of the graph. The implementation,
however, uses a directed graph.
- ...
- for the sake of
simplicity, several details like the propagation of segment
information or the quadtree administration must be omitted.
- ...
- Through repreated grid
merge operations the number of grid points in the wafer state grid
may grow considerably, so that the removal of grid points becomes
necessary
- ...
- This implies a
data redundancy of a factor of 2 which is accepted for the benefit
of consistency verifications and speed advantages
- ...
- In most practical cases the depth hardly exceeds 6.
- ...
- To avoid confusion, one should distinguish between
internal computational (simulation) grids which, depending on
models and abstractions, need not necessarily be geometry-conform and global
static grids which are used to define spatially varying
properties within given spatial structures.
- ...
- To be
more precise, certain common assumptions [95]
about the configuration of
the points in
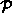 have to be made, like the exclusion of
collinear or cocircular point
subsets. However, these assumptions are only relevant for theoretical
considerations as they exclude many important practical applications.
have to be made, like the exclusion of
collinear or cocircular point
subsets. However, these assumptions are only relevant for theoretical
considerations as they exclude many important practical applications.
- ...
- The GRS
will be part of another text.
- ...
- the evaluation reflects
the status VORONOI as of 1993-12-22
- ...
- A refinement
with a minimum number of boundary grid points can only be expected
when a sufficient and necessary criterion for edge refinement
(like, e.g. Theorem 6.5) is used.
- ...
- Note that all
process parameters that may be given are simulation parameters as
the real processing parameters are not available.
- ...
- The source code size of the etch and deposit
simulation module of VISTA [141] is 210kB
- ...
- VORONOI has a source code size of 280kB
- ...
- The application itself is entirely coded
in C
- ...
- Due to their remarkable
success (which is partly due to the rather
narrow focus), the simulators are still in use today.
Martin Stiftinger
Thu Oct 13 13:51:43 MET 1994
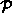 have to be made, like the exclusion of
collinear or cocircular point
subsets. However, these assumptions are only relevant for theoretical
considerations as they exclude many important practical applications.
have to be made, like the exclusion of
collinear or cocircular point
subsets. However, these assumptions are only relevant for theoretical
considerations as they exclude many important practical applications.
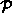 have to be made, like the exclusion of
collinear or cocircular point
subsets. However, these assumptions are only relevant for theoretical
considerations as they exclude many important practical applications.
have to be made, like the exclusion of
collinear or cocircular point
subsets. However, these assumptions are only relevant for theoretical
considerations as they exclude many important practical applications.