References





Next: List of Publications
Up: PhD Thesis Stefan Halama
Previous: 8.6.6 VORONOI as General-Purpose
References
- 1
-
P. Freeman.
Fundamentals of Design.
In Tutorial on Software Design Techiques, Fourth Edition, pp
2-22, Los Alamitos, California, 1983. IEEE Computer Society Press.
- 2
-
S. Kleinfeldt, M. Guiney, J.K. Miller, and M. Barnes.
Design Methodology Management.
Proc.IEEE, 82(2):231-250, 1994.
- 3
-
T.J. Barnes, D. Harrison, A.R. Newton, and R.L. Spickelmier.
Electronic CAD Frameworks.
Kluwer, 1992.
- 4
-
F. Fasching, S. Halama, and S. Selberherr, editors.
Technology CAD Systems. Springer, 1993.
- 5
-
P. Lloyd, E.J. Prendergast, and K. Shinghal.
Technology CAD for Competitive Products.
In G. Baccarani and M. Rudan, editors, Simulation of
Semiconductor Devices and Processes, volume 3, pp 111-126, Bologna, 1988.
Tecnoprint.
- 6
-
P. Lloyd, H.K. Dirks, E.J. Prendergast, and K. Singhal.
Technology CAD for Competitive Products.
IEEE Trans.Computer-Aided Design, 9(11):1209-1216, 1990.
- 7
-
P. Lloyd, C.C. McAndrew, M.J. McLennan, S. Nassif, K. Singhal, Ku. Singhal,
P.M. Zeitzoff, M.N. Darwish, K. Haruta, J.L. Lentz, H. Vuong, M.R. Pinto,
C.S. Rafferty, and I.C. Kizilyalli.
Technology CAD at AT&.
In Fasching et al. [4], pp 1-24.
- 8
-
D.M.H. Walker, C.S. Kellen, and A.J. Strojwas.
The PREDITOR Process Editor and Statistical Simulator.
In Proc.VPAD, pp 120-121, 1991.
- 9
-
D.M.H. Walker, J.K. Kibarian, Ch.S. Kellen, and A.J. Strojwas.
A TCAD Framework for Development and Manufacturing.
In Fasching et al. [4], pp 83-112.
- 10
-
D.M.H. Walker, Ch.S. Kellen, D.M. Svoboda, and A.J. Strojwas.
The CDB/HCDB Semiconductor Wafer Representation Server.
IEEE Trans.Computer-Aided Design, 12(2):283-295, 1993.
- 11
-
H. Matsuo, H. Masuda, S. Yamamoto, and T. Toyabe.
A Supervised Process and Device Simulation for Statistical VLSI
Design.
In Proc.NUPAD III, pp 59-60, 1990.
- 12
-
R.W. Knepper, J.B. Johnson, S. Furkay, J. Slinkman, X. Tian, E.M. Buturla,
R. Young, G. Fiorenza, R. Logan, Y.S. Huang, R.R. O'Brien, C.S. Murthy, P.C.
Murley, J. Peng, H.H.K. Tang, G.R. Srinivasan, M.M. Pelella, D.A. Sunderland,
J. Mandelman, D. Lieber, E. Farrell, and M. Kurasic.
Technology CAD at IBM.
In Fasching et al. [4], pp 25-62.
- 13
-
J. Mar, K. Bhargavan, S.G. Duvall, R. Firestone, D.J. Lucey, S.N. Nandgaonkar,
Wu S., Yu K.S., and Zarbakhsh F.
EASE - An Application-Based CAD System for Process Design.
IEEE Trans.Computer-Aided Design, CAD-6(6):1032-1038, 1987.
- 14
-
J. Mar.
Technology CAD at Intel.
In Fasching et al. [4], pp 63-74.
- 15
-
D.S. Boning, M.B. McIlrath, P. Penfield Jr., and E.M. Sachs.
A General Semiconductor Process Modeling Framework.
IEEE Trans.Semiconductor Manufacturing, 5(4):266-280, 1992.
- 16
-
N. Tanabe.
Technology CAD at NEC.
In Fasching et al. [4], pp 237-254.
- 17
-
K. Nishi and J. Ueda.
Technology CAD at OKI.
In Fasching et al. [4], pp 255-274.
- 18
-
P.A. Gough, M.K. Johnson, P. Walker, and H. Hermans.
An Integrated Device Design Environment for Semiconductors.
IEEE Trans.Computer-Aided Design, 10(6):808-821, 1991.
- 19
-
P.A. Gough.
An Integrated Design Environment for Semiconductors.
In Fasching et al. [4], pp 131-146.
- 20
-
M.R. Simpson.
PRIDE: An Integrated Design Environment for Semiconductor Device
Simulation.
In Proc.NUPAD III, pp 57-58, Honolulu, Hawaii, 1990.
- 21
-
M.R. Simpson.
PRIDE: An Integrated Design Environment for Semiconductor Device
Simulation.
IEEE Trans.Computer-Aided Design, 10(9):1163-1174, 1991.
- 22
-
H. Jacobs, W. Hänsch, F. Hofmann, W. Jacobs, M Paffrath, E. Rank,
K. Steger, and U. Weinert.
SATURN - A Device Engineer's Tool for Optimizing MOSFET
Performance and Lifetime.
In Proc.NUPAD III, pp 55-56, 1990.
- 23
-
W. Jacobs.
The SATURN Technology CAD System.
In Fasching et al. [4], pp 147-162.
- 24
-
P.J. Hopper and P.A. Blakey.
The MASTER Framework.
In Fasching et al. [4], pp 275-292.
- 25
-
J. Lorenz, C. Hill, H. Jaouen, C. Lombardi, C. Lyden, K. De Meyer, J. Pelka,
A. Poncet, M. Rudan, and S. Solmi.
The STORM Technology CAD System.
In Fasching et al. [4], pp 163-196.
- 26
-
R.W. Dutton and R.J.G. Goossens.
Technology CAD at Stanford University: Physics, Algorithms, Software,
and Applications.
In Fasching et al. [4], pp 113-130.
- 27
-
V. Axelrad, Y. Granik, and R. Jewell.
CAESAR: The Virtual IC Factory as an Integrated TCAD User
Environment.
In Fasching et al. [4], pp 293-307.
- 28
-
V. Axelrad.
CAESAR 1.1 Released.
Technical Report 1, Technology Modeling Associates, Inc., Palo Alto,
California, 1994.
- 29
-
K.S.V. Gopalarao, P.K. Mozumder, and D.S. Boning.
An Integrated Technology CAD System for Process and Device Designers.
IEEE Trans.VLSI Systems, 1(4):482-490, 1993.
- 30
-
K. Kato, N. Shigyo, T. Wada, S. Onga, M. Konaka, and Taniguchi K.
A Supervised Simulation System for Process and Device Design Based on
a Geometrical Data Interface.
IEEE Trans.Electron Devices, ED-34(10):2049-2058, 1987.
- 31
-
H. Pimingstorfer, S. Halama, S. Selberherr, K. Wimmer, and P. Verhas.
A Technology CAD Shell.
In Fichtner and Aemmer [148], pp 409-416.
- 32
-
F. Fasching, C. Fischer, S. Halama, H. Pimingstorfer, H. Read, S. Selberherr,
H. Stippel, W. Tuppa, P. Verhas, and K. Wimmer.
A New Open Techology CAD System.
Microelectronic Engineering, pp 217-220, 1991.
- 33
-
S. Halama, F. Fasching, H. Pimingstorfer, W. Tuppa, and S. Selberherr.
Consistent User Interface and Task Level Architecture of a TCAD
System.
In Proc.NUPAD IV, pp 237-242, 1992.
- 34
-
S. Halama, F. Fasching, C. Fischer, H. Kosina, E. Leitner, Ch. Pichler,
H. Pimingstorfer, H. Puchner, G. Rieger, G. Schrom, T. Simlinger,
M. Stiftinger, H. Stippel, E. Strasser, W. Tuppa, K. Wimmer, and
S. Selberherr.
The Viennese Integrated System for Technology CAD Applications.
In Fasching et al. [4], pp 197-236.
- 35
-
A.S. Wong, D.S. Boning, M.L. Heytens, and A.R. Neureuther.
The Intertool Profile Interchange Format.
In Proc.NUPAD III, pp 61-62, Honolulu, Hawaii, 1990.
- 36
-
A.S. Wong.
Technology Computer-Aided Design Frameworks and the PROSE
Implementation.
PhD thesis, University of California, Berkeley, 1992.
- 37
-
A.S. Wong and A.R. Neureuther.
The Intertool Profile Interchange Format: A Technology CAD
Environment Approach.
IEEE Trans.Computer-Aided Design, 10(9):1157-1162, 1991.
- 38
-
E.W. Scheckler, A.S. Wong, R.H. Wang, G. Chin, J.R. Camanga, A.R. Neureuther,
and R.W. Dutton.
A Utility-Based Integrated System for Process Simulation.
IEEE Trans.Computer-Aided Design, 11(7):911-920, 1992.
- 39
-
R.H. Wang, A. Gabara, and A.R. Neureuther.
BTU - Berkeley Topography Utilities for Linking Topography and
Impurity Profile Simulations.
In Proc.NUPAD IV, pp 237-242. IEEE Catalog Number 92TH0424-2,
1992.
- 40
-
F.P. Brooks.
The Mythical Man-Month: Essays on Software Engineering.
Addison-Wesley, 1982.
- 41
-
C.H. Corbex, A.F. Gerodolle, S.P. Martin, and A.R. Poncet.
Data structuring for process and device simulations.
IEEE Trans.Computer-Aided Design, CAD-7:489-500, 1988.
- 42
-
S.G. Duvall.
An Interchange Format for Process and Device Simulation.
IEEE Trans.Computer-Aided Design, CAD-7(7):741-754, 1988.
- 43
-
D.S. Boning, M.L. Heytens, and A.S. Wong.
The Intertool Profile Interchange Format: An Object-Oriented
Approach.
IEEE Trans.Computer-Aided Design, 10(9):1150-1156, 1991.
- 44
-
F. Fasching, W. Tuppa, and S. Selberherr.
VISTA - The Data Level.
IEEE Trans.Computer-Aided Design, 13(1):72-81, 1994.
- 45
-
SWR Working Group of the CFI/TCAD TSC.
Semiconductor Wafer Representation Architecture.
CAD Framework Initiative, Austin, Texas, USA, 1.0 edition, 1992.
- 46
-
D. Boning, G. Chin, R. Cottle, W. Dietrich, S. Duvall, M. Giles, R. Harris,
M. Karasick, N. Khalil, M. Law, M.J.McLennan, P.K. Mozumder, L. Nackman,
S. Nassif, V.T. Rajan, D. Schröder, R. Tremain, D.M.H. Walker, R. Wang,
and A. Wong.
Developing and Integrating TCAD Applications with the Semiconductor
Wafer Representation.
In Proc.NUPAD IV, pp 199-204, 1992.
- 47
-
K.M. DeMeyer, R. Cartuyvels, and L. Dupas.
A Simulation Strategy for Process Optimization.
In Proc.VPAD, pp 80-81, 1993.
- 48
-
J.K. Ousterhout.
Tcl: An Embeddable Command Language.
In 1990 Winter USENIX Conference Proceedings, pp 133-146,
1990.
- 49
-
K. Funakoshi and K. Mizuno.
A Rule-Based VLSI Process Flow Validation System With Macroscopic
Process Simulation.
IEEE Trans.Semiconductor Manufacturing, 3(4):239-246, 1990.
- 50
-
J. Daniell and S.W. Director.
An Object Oriented Approach to CAD Tool Control.
IEEE Trans.Computer-Aided Design, 10(6):698-713, 1991.
- 51
-
J.K. Ousterhout.
An X11 Toolkit Based on the Tcl Language.
In 1991 Winter USENIX Conference Proceedings, pp 105-115,
1991.
- 52
-
L. Maliniak.
CAD Frameworks Ride a Rough Road To Success.
Electronic Design, pp 36-42, 1992.
- 53
-
M. van Genuchten.
Why is Software Late? An Empirical Study of Reasons for Delay in
Software Development.
IEEE Trans.Software Engineering, 17(6):582-590, 1991.
- 54
-
S.M. Rubin.
A General-Purpose Framework for CAD Algorithms.
IEEE Communications Mag., pp 56-62, 1991.
- 55
-
R.W. Scheifler, J. Gettys, and R. Newman.
X Window System: C Library and Protocol Reference.
Digital, 1988.
- 56
-
A.I. Wasserman.
Tool Integration in Software Engineering Environments.
In Software Engineering Environments, number 467 in Lecture
Notes in Computer Science, pp 137-149, New York, 1989. Springer.
- 57
-
A. Earl.
Principles of a Reference Model for Computer Aided Software
Engineering Environments.
In Software Engineering Environments, number 467 in Lecture
Notes in Computer Science, pp 115-129, New York, 1989. Springer.
- 58
-
I.Thomas and B.A. Nejmeh.
Definitions of Tool Integration for Environments.
IEEE Software, 9(2):29-35, 1992.
- 59
-
F. Straker and S. Selberherr.
Capacitance Computation for VLSI Structures.
In Proc. EUROCON, pp 602-608, 1986.
- 60
-
H. Kosina and S. Selberherr.
A Hybrid Device Simulator that Combines Monte Carlo and
Drift-Diffusion Analysis.
IEEE Trans.Computer-Aided Design, 13(1):Scheduled for
publication, 1994.
- 61
-
G. Hobler, S. Halama, W. Wimmer, S. Selberherr, and H. Pötzl.
RTA-Simulations with the 2-D Process Simulator PROMIS.
In Proc.NUPAD III, pp 13-14, 1990.
- 62
-
M.E. Law and R.W. Dutton.
Verification of Analytic Point Defect Models Using SUPREM-IV.
IEEE Trans.Computer-Aided Design, 7(2):181-190, 1988.
- 63
-
A.R. Neureuther.
IC Process Modeling and Topography Design.
Proc.IEEE, 71(1):121-128, 1983.
- 64
-
Make A Program for Maintaining Computer Programs.
S.I. Feldman.
Software - Practice and Experience, 9:255-265, 1979.
- 65
-
D. Heimbigner and S. Krane.
A Graph Transform Model for Configuration Management Environments.
ACM SigPLAN Notices, 24(2):216-225, 1989.
- 66
-
A. Mahler and A. Lampen.
An Integrated Toolset for Engineering Software Configurations.
ACM SigPLAN Notices, 24(2):216-225, 1989.
- 67
-
R. Stallman and R. McGrath.
GNU make, Version 3.63, 1993.
- 68
-
T. Brunhoff and J. Folton.
imake - C preprocessor interface to the make utility.
X11R4 and X11R5 release.
- 69
-
J.R. Callahan and J.M. Purtilo.
A Packing System for Heterogeneous Execution Environments.
IEEE Trans.Software Engineering, 17(6):626-635, 1991.
- 70
-
E.A. Ipser, D.S. Wile, and D.Jacobs.
A Multi-Formalism Specification Environment.
ACM SIGSOFT Software Engineering Notes, 14(2):25-31, 1989.
- 71
-
F. Fasching, C. Fischer, S. Selberherr, H. Stippel, W. Tuppa, and H. Read.
A PIF Implementation for TCAD Purposes.
In Fichtner and Aemmer [148], pp 477-482.
- 72
-
P.H. Winston and B.K.P. Horn.
Lisp.
Addison-Wesley, 1989.
- 73
-
A. Nye.
Xlib Programming Manual, volume 1.
O'Reilly & Associates, 1988.
- 74
-
P.J. Asente and R.R. Swick.
X Window System Toolkit, The Complete Programmer's Guide and
Specification.
Digital Press, 1990.
- 75
-
OSF/Motif Programmer's Guide, Release 1.1, 1991.
- 76
-
M.A. Linton, J.M. Vlissides, and P.R. Calder.
Composing User Interfaces with InterViews.
IEEE Computer, pp 8-22, 1989.
- 77
-
N. Mayer.
WINTERP: An object-oriented rapid prototyping, development and
delivery environment for building user-customizable applications with the
OSF/Motif UI Toolkit.
Technical report, Hewlett-Packard Laboratories, Palo Alto, 1991.
- 78
-
R. Hesketh.
The Dirt User Interface Builder, 1990.
- 79
-
J.D. Foley.
Computer Graphics.
Addison-Wesley, 1942.
- 80
-
B.A. Myers.
User-Interface Tools: Introduction and Survey.
IEEE Software, pp 15-23, 1989.
- 81
-
R. Stallman.
GNU Emacs Manual, 1986.
- 82
-
AUTOCAD Release 11 Reference Manual, 1990.
Publication AC11RM.E1.
- 83
-
A. Neureuther, R. Wang, and J. Helmsen.
Perspective on TCAD Integration at Berkeley.
In Fasching et al. [4], pp 75-82.
- 84
-
D.M. Betz.
XLISP: An Object-Oriented Lisp, Version 2.1, 1989.
- 85
-
J. Rumbaugh, M. Blaha, W. Premerlani, F. Eddy, and W. Lorensen.
Object-Oriented Modeling and Design.
Prentice-Hall International Editions, 1991.
- 86
-
Ch. Pichler and S. Selberherr.
Process Flow Representation within the VISTA Framework.
In Selberherr et al. [147], pp 25-28.
- 87
-
H. Masuda, H. Pimingstorfer, H. Sato, K. Tsuneno, K. Ichikawa, H. Tobe,
H. Miyazawa, M. Nakamura, K. Kajigaya, O. Tsuchiya, and T. Matsumoto.
Applied TCAD in Mega-Bits Memory Design.
In Selberherr et al. [147], pp 21-24.
- 88
-
H. Pimingstorfer.
Integration und Anwendung von Simulatoren in der CMOS-Entwicklung.
Dissertation, Technische Universität Wien, 1993.
- 89
-
C.D. Potter.
FEA to the Core.
Computer Graphics World, 16(5):21-24, 1993.
- 90
-
R.H. Wolfe, M. Needels, T. Arias, and J.D. Joannopoulos.
Visual Revelations from Silicon Ab Initio Calculations.
IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications, 35(1):45-53, 1992.
- 91
-
K. Koyamada and T. Nishio.
Volume Visualization of 3D Finite Element Method Results.
IBM J.Res.Dev., 35(1):12-25, 1991.
- 92
-
A. Emmett.
Something for Everybody.
Computer Graphics World, 16(5):29-41, 1993.
- 93
-
H. Bienenstein.
Darstellung von Funktionen dreier Veränderlicher mittels einer
Tetraeder-Struktur.
Diplomarbeit, Technische Universität Wien, 1992.
- 94
-
H. Stippel.
Simulation der Ionen-Implantation.
Dissertation, Technische Universität Wien, 1993.
- 95
-
F.P. Preparata and M.I. Shamos.
Computational Geometry.
Springer, 1985.
- 96
-
W.H. Chu.
Development of a General Finite Difference Approximation for a
General Domain.
Journal of Computational Physics, 8:392-408, 1971.
- 97
-
W.D. Barfield.
Numerical Method for Generating Orthogonal Curvilinear Meshes.
Journal of Computational Physics, 5:23-33, 1970.
- 98
-
W.D. Barfield.
An Optimal Mesh Generator for Lagrangian Hydrodynamic Calculations in
Two Space Dimensions.
Journal of Computational Physics, 6:417-429, 1970.
- 99
-
J.E. Castillo.
Mathematical Aspects of Numerical Grid Generation.
SIAM, Philadelphia, 1991.
- 100
-
K. Wimmer, R. Bauer, S. Halama, G. Hobler, and S. Selberherr.
Transformation Mehods for Nonplanar Process Simulation.
In Fichtner and Aemmer [148], pp 120-121.
- 101
-
Z.M.V. Kovács and M. Rudan.
Boundary Fitted Coordinate Generation for Device Analysis on
Composite and Complicated Geometries.
IEEE Trans.Computer-Aided Design, 10(10):1242-1250, 1991.
- 102
-
S.P. Chin and C.Y Wu.
A New Grid-Generation Method for 2-D Simulation of Devices with
Nonplanar Semiconductor Surface.
IEEE Trans.Computer-Aided Design, 12(9):1337-1344, 1993.
- 103
-
P. Ciampolini, A. Forghieri, A. Pierantoni, A. Gnudi, M.V. Rudan, and
G. Baccarani.
Adaptive Mesh Generation Preserving the Quality of the Initial Grid.
IEEE Trans.Computer-Aided Design, CAD-8(5):490-500, 1989.
- 104
-
R. Ismail and G. Amaratunga.
Adaptive Meshing Schemes for Simulating Dopant Diffusion.
IEEE Trans.Computer-Aided Design, 9(3):276-289, 1990.
- 105
-
J.F. Bürgler, W.M. Coughran Jr., and W. Fichtner.
An Adaptive Grid Refinement Strategy for the Drift-Diffusion
Equations.
IEEE Trans.Computer-Aided Design, 10(10):1251-1258, 1991.
- 106
-
S. Müller, K. Kells, and W. Fichtner.
Automatic Rectangle-Based Adaptive Mesh Generation without Obtuse
Angles.
IEEE Trans.Computer-Aided Design, CAD-11(7):855-863, 1992.
- 107
-
D. Yang, R.W. Dutton, and K.H. Law.
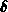 -Zone Triangulation: A Boundary Refinement Scheme For
Quadtree Based Mesh.
In Proc.VPAD, pp 120-121, Nara, Japan, 1993.
-Zone Triangulation: A Boundary Refinement Scheme For
Quadtree Based Mesh.
In Proc.VPAD, pp 120-121, Nara, Japan, 1993.
- 108
-
Z.H. Sahul, R.W. Dutton, and M. Noell.
Grid and Geometry Techniques for Multi-Layer Process Simulation.
In Selberherr et al. [147], pp 417-420.
- 109
-
C. Fischer, G. Nanz, and S. Selberherr.
Finite Difference, Boundary-Fitted Grid Generation for Arbitrarily
Shaped Two-Dimensional Simulation Areas.
Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering,
110:17-24, 1993.
- 110
-
N. Hitschfeld, P. Conti, and W. Fichtner.
Mixed Element Trees: A Generalization of Modified Octrees for the
Generation of Meshes for the Simulation of Complex 3-D Semiconductor Device
Structures.
IEEE Trans.Computer-Aided Design, 12(11):1714-1725, 1993.
- 111
-
V. Srinivasan, L. Nackman, J. Tang, and S. Meshkat.
Automatic Mesh Generation Using the Symmetric Axis Transformation of
Polygonal Domains.
Proc.IEEE, 80(9):1485-1501, 1992.
- 112
-
B. Baccus, D. Collard, and E. Dubois.
Adaptive Mesh Refinement for Multilayer Process Simulation Using the
Finite Element Method.
IEEE Trans.Computer-Aided Design, 11(3):396-403, 1992.
- 113
-
R.E. Bank.
PLTMG: A Software Package for Solving Elliptic Partial
Differential.
SIAM, Philadelphia, 1990.
- 114
-
W.M. Coughran Jr., M.R. Pinto, and R.K. Smith.
Adaptive Grid Generation for VLSI Device Simulation.
IEEE Trans.Computer-Aided Design, 10(10):1259-1275, 1991.
- 115
-
M.E. Agishtein and A.A. Migdal.
Smooth Surface Reconstruction from Scattered Data Points.
Comput. & Graphics, 15(1):29-39, 1991.
- 116
-
L.L. Schumaker.
Triangulations in CAGD.
IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications, 13(1):47-52, 1993.
- 117
-
S. Halama, K. Wimmer, G. Hobler, and S.Selberherr.
Finite-Differenzen Dreiecksnetzgenerierung für die
Prozeßsimulation mit PROMIS.
In NuTech, p 3, Garmisch-Partenkirchen, Germany, 1990.
- 118
-
S. Halama, G. Hobler, K. Wimmer, and S.Selberherr.
Eine neue Methode zur Simulation der Diffusion in allgemeinen
Strukturen.
In Grundlagen und Technologie elektronischer Bauelemente, pp
20-26, Gesellschaft für Mikroelektronik, Vienna, Austria, 1991.
- 119
-
H. Samet.
The Design and Analysis of Spatial Data Structures.
Addison-Wesley, 1990.
- 120
-
P.J. Green and R.Sibson.
Computing Dirichlet Tesselations in the Plane.
The Computer Journal, 21(2):168-173, 1978.
- 121
-
R. Sibson.
Locally Equiangular Triangulations.
The Computer Journal, 21(3):243-245, 1978.
- 122
-
D.T. Lee and B.J. Schachter.
Two Algorithms for Constructing a Delaunay Triangulation.
International Journal of Computer and Information Sciences,
9(3):219-242, 1980.
- 123
-
S. Saxena, P.C.P. Bhatt, and V.C. Prasad.
Efficient VLSI Parallel Algorithm for Delaunay Triangulation on
Orthogonal Tree Network in Two and Three Dimensions.
IEEE Trans.Computers, 39(3):400-404, 1990.
- 124
-
F.W. Wilson, R.K. Goodrich, and W. Spratte.
Lawson's Triangulation is Nearly Optimal for Controlling Error
Bounds.
SIAM J.Numer.Anal., 27(1):190-197, 1990.
- 125
-
O. Palacios-Velez and B. C. Renaud.
A Dynamic Hierarchical Subdivision Algorithm for Computing Delaunay
Triangulations and Other Closest-Point Problems.
ACM Trans.Mathematical Software, 15(3):257-292, 1990.
- 126
-
K. Sugihara and M. Iri.
Construction of the Voronoi Diagram for ``One Million'' Generators in
Single-Precision Arithmetic.
Proc.IEEE, 80(9):1471-1484, 1992.
- 127
-
S. Rippa.
Long and Thin Triangles can be Good for Linear Interpolation.
SIAM J.Numer.Anal., 29(1):252-270, 1992.
- 128
-
T.P. Fang and L.A. Piegl.
Delaunay Triangulation Using a Uniform Grid.
IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications, 13(3):36-47, 1993.
- 129
-
H. Edelsbrunner, T.S. Tan, and R. Waupotitsch.
An
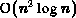 -Time Algorithm for the MINMAX Angle
Triangulation.
SIAM J.Sci.Stat.Comput., 13(4):994-1008, 1992.
-Time Algorithm for the MINMAX Angle
Triangulation.
SIAM J.Sci.Stat.Comput., 13(4):994-1008, 1992.
- 130
-
A. Bowyer.
Computing Dirichlet Tesselations.
The Computer Journal, 24(2):162-166, 1990.
- 131
-
B. Joe.
Construction of Three-Dimensional Delaunay Triangulations Using Local
Transformations.
Computer Aided Geometric Design, 8:123-142, 1991.
- 132
-
D.F. Watson.
Computing the n-Dimensional Delaunay Tesselation with Application to
Voronoi Polytopes.
The Computer Journal, 24(2):167-172, 1981.
- 133
-
O.J. Murphy.
Nearest Neighbour Pattern Classification Perceptrons.
Proc.IEEE, 78(10):1595-1990, 1990.
- 134
-
R. Laurini and D. Thompson.
Fundamentals of Spatial Information Systems.
Academic Press, 1992.
- 135
-
K. Sugihara.
An Intersection Algorithm Based on Delaunay Triangulation.
IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications, 12(2):59-67, 1992.
- 136
-
G.M. Nielson.
Scattered Data Modeling.
IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications, 13(1):60-70, 1993.
- 137
-
H. Akima.
A New Method of Interpolation and Smooth Curve Fitting Based on Local
Procedures.
J.ACM, 17(4):589-602, 1970.
- 138
-
J.M. Hyman.
Accurate Monotonicity Preserving Cubic Interpolation.
SIAM J.Sci.Stat.Comput., 4(4):645-654, 1983.
- 139
-
D.S.Wen, W.H. Chang, Y. Lii, A.C. Megdanis, P. McFarland, and G.Bronner.
A Fully Planarized
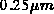 CMOS Technology.
In Proc.Symposium on VLSI Technology, pp 83-84, 1991.
CMOS Technology.
In Proc.Symposium on VLSI Technology, pp 83-84, 1991.
- 140
-
B. Davari, C.W. Koburger, R. Schulz, J.D. Warnock, T. Furukawa, W.Jost, W.G.
Schwittek, J.K. DeBrosse, M.L. Kerbaugh, and J.L. Mauer.
A New Planarization Technique, Using a Combination of RIE and
Chemical Mechanical Polish (CMP).
In Int.Electron Devices Meeting, pp 61-64, 1989.
- 141
-
E. Strasser and S. Selberherr.
A General Simulation Method for Etching and Deposition Processes.
In Selberherr et al. [147], pp 357-360.
- 142
-
Technology Modeling Associates, Inc.
TMA TSUPREM-4, Two-Dimensional Process Simulation Program
Version 6, 1993.
- 143
-
T. Miyoshi and M. Azuma.
An Empirical Study of Evaluating Software Development Environment
Quality.
IEEE Trans.Software Engineering, pp 425-435, 1993.
- 144
-
P. Freeman.
Reusable Software Engineering: Concepts and Research Directions.
In Tutorial on Software Design Techiques, Fourth Edition, pp
63-76, Los Alamitos, California, 1983. IEEE Computer Society Press.
- 145
-
R.W. Dutton.
Another Look at TCAD - Challenges of the 1990's.
In Proc.VPAD, pp 1-3, 1991.
- 146
-
E.J. Weyuker.
Evaluating Software Complexity Measures.
IEEE Trans.Software Engineering, 14(9):1357-1365, 1988.
- 147
-
S. Selberherr, H. Stippel, and E. Strasser, editors.
Simulation of Semiconductor Devices and Processes, volume 5.
Springer, 1993.
- 148
-
W. Fichtner and D. Aemmer, editors.
Simulation of Semiconductor Devices and Processes, volume 4,
Konstanz, 1991. Hartung-Gorre.
Martin Stiftinger
Thu Oct 13 13:51:43 MET 1994
 -Zone Triangulation: A Boundary Refinement Scheme For
Quadtree Based Mesh.
In Proc.VPAD, pp 120-121, Nara, Japan, 1993.
-Zone Triangulation: A Boundary Refinement Scheme For
Quadtree Based Mesh.
In Proc.VPAD, pp 120-121, Nara, Japan, 1993.
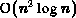 -Time Algorithm for the MINMAX Angle
Triangulation.
SIAM J.Sci.Stat.Comput., 13(4):994-1008, 1992.
-Time Algorithm for the MINMAX Angle
Triangulation.
SIAM J.Sci.Stat.Comput., 13(4):994-1008, 1992.
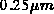 CMOS Technology.
In Proc.Symposium on VLSI Technology, pp 83-84, 1991.
CMOS Technology.
In Proc.Symposium on VLSI Technology, pp 83-84, 1991.




