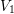 to
to 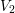 is
obtained from the binding energy,
is
obtained from the binding energy, 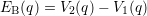 . This energy writes as
. This energy writes as
In a radiative process the energy necessary for a transition from 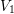 to
to 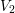 is
obtained from the binding energy,
is
obtained from the binding energy, 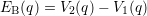 . This energy writes as
. This energy writes as
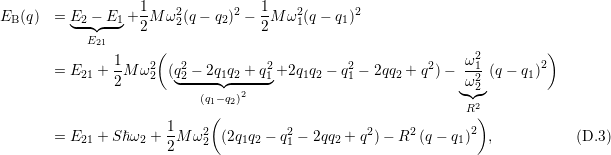
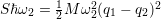 from
from 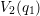 to
to 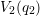 .
The two points where a radiative transition is possible after the Franck-Condon
principle are at
.
The two points where a radiative transition is possible after the Franck-Condon
principle are at 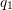 and
and 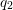 . Inserting yields
. Inserting yields 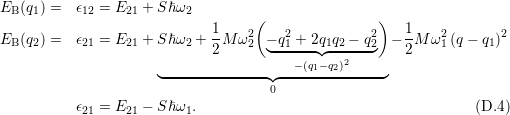
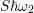 ,
, 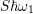 is defined as the relaxation energy from
is defined as the relaxation energy from 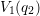 to
to 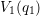 . A full MPE process is schematically depicted in Fig. D.1 for
quadratic coupling (
. A full MPE process is schematically depicted in Fig. D.1 for
quadratic coupling (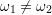 ). In the case of linear coupling (
). In the case of linear coupling (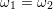 ) both
relaxation energies coincide.
) both
relaxation energies coincide.
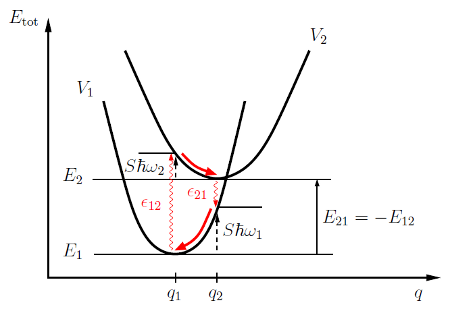
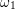 and
and
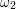 in a reaction coordinate diagram. The photon energy required to change
from
in a reaction coordinate diagram. The photon energy required to change
from 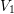 to
to 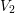 equals
equals 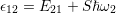 . Due to structural relaxation,
the photon emitted in the following reverse process is smaller, namely
. Due to structural relaxation,
the photon emitted in the following reverse process is smaller, namely
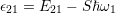 .
.