

Next: 6.2.3 Gridding Structures Generated
Up: 6.2 Topography Simulation
Previous: 6.2.1 Solid Modeling
6.2.2 Constructing a Grid
The final objective is obtaining a grid suitable for finite-element
simulators. For layered structures a robust gridding method can be achieved
using a reliable two-dimensional meshing tool. To do so, in the stacking
process all faces of one layer are merged into a single two-dimensional
geometry, that is gridded with well proofed tools to generate a triangular
mesh.
The resulting triangles are then extruded to prismatic elements (with the height
of the layer), and finally, a three-dimensional grid is obtained by
splitting each prismatic element into three tetrahedral cells. The
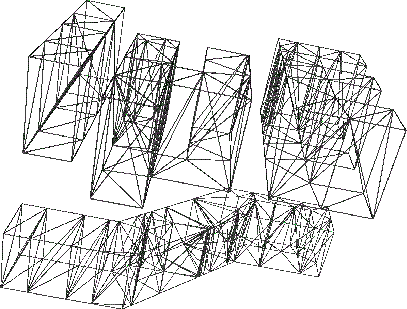
result from the tool laygrid [68] based on this algorithm applied
to the 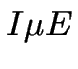 -logo layout is shown in Figure 6.8 (note that the
very coarse grid is intentional). This program uses a modified
version of Bank's mesher trigen [69] or (at user's choice)
Shewchuk's triangle [70].
-logo layout is shown in Figure 6.8 (note that the
very coarse grid is intentional). This program uses a modified
version of Bank's mesher trigen [69] or (at user's choice)
Shewchuk's triangle [70].
Figure 6.8:
Grid of the 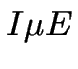 -logo example.
-logo example.
 |
Rui Martins
1999-02-24
![]() -logo layout is shown in Figure 6.8 (note that the
very coarse grid is intentional). This program uses a modified
version of Bank's mesher trigen [69] or (at user's choice)
Shewchuk's triangle [70].
-logo layout is shown in Figure 6.8 (note that the
very coarse grid is intentional). This program uses a modified
version of Bank's mesher trigen [69] or (at user's choice)
Shewchuk's triangle [70].