In this model the materials are treated as elastic solids
parameterized by their Young Modulus E and Poisson ratio ![]() . The
stress tensor is calculated uniquely from the strain tensor which is
solved from the Navier Stokes equations [Zie91] together with the
displacement boundary conditions.
. The
stress tensor is calculated uniquely from the strain tensor which is
solved from the Navier Stokes equations [Zie91] together with the
displacement boundary conditions.
In theory of linear elasticity with small displacements the strain
tensor can be defined as
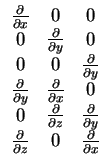
|
(5.1) |
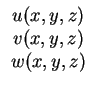
|
(5.2) |
Assuming a linear material law, the stress tensor can now be
calculated using the equation
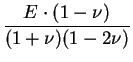 . . 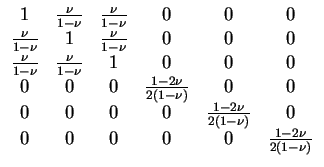
|
(5.4) |
Introducing the distributed body forces
f (x, y, z) = 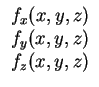
|
(5.5) |
| (5.6) | |||
| (5.7) | |||
| (5.8) |