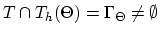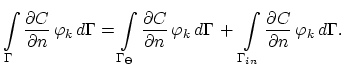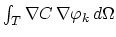


Next: 5 Numerical Handling of
Up: 8 Numerical Handling of
Previous: 3 Discretization of the
In order to assess the numerical scheme for the problem described in Section 3.5.3 it is useful to construct
an analytical solution for a special one-dimensional case. For the sake of simplicity, we consider in both segments intrinsic diffusion (Section 3.3.1).
As segment 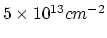 the region
the region 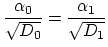 is assumed and as segment
is assumed and as segment  region
region 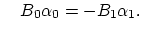 .
The one-dimensional segregation problem fullfils the following initial and interface conditions,
.
The one-dimensional segregation problem fullfils the following initial and interface conditions,
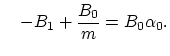 and and |
(181) |
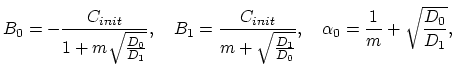 at interface at interface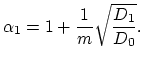 |
(182) |
Note that condition (3.117) also means that the media from both sides
of the interface has an infinite length.
We are searching for the solution of the problem given by (3.30), (3.117),
(3.118) and (3.119) in the form,
for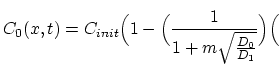 |
(183) |
for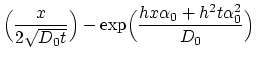 |
(184) |
where
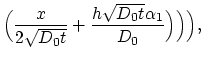 are constants to be
determined and
are constants to be
determined and
is a solution of the diffusion equation (
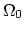 ) for the
case of the surface evaporation condition already
studied in [38].
) for the
case of the surface evaporation condition already
studied in [38].
We determine constants
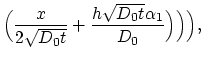 from the initial and interface conditions
(3.117), (3.118), (3.119) as follows.
From the initial conditions we have
from the initial and interface conditions
(3.117), (3.118), (3.119) as follows.
From the initial conditions we have
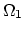 and and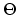 |
|
|
(186) |
The interface condition (3.119) yields
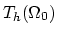 |
(187) |
This equation is fullfiled if
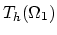 and and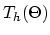 |
|
|
(188) |
From (3.118) and (3.123) follows,
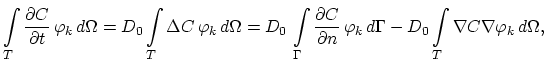 erfc erfc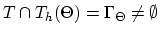 |
(189) |
The last equality is ensured for the condition,
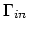 and and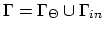 |
|
|
(190) |
By solving the equation system given by (3.125) and
(3.127) we have,
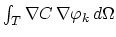 |
(191) |
So we can write a solution for the problem posed by (3.30), (3.117),
(3.118) and (3.119). For 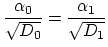 ,
,
and for 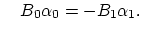 ,
,



Next: 5 Numerical Handling of
Up: 8 Numerical Handling of
Previous: 3 Discretization of the
J. Cervenka: Three-Dimensional Mesh Generation for Device and Process Simulation
![]() the region
the region ![]() is assumed and as segment
is assumed and as segment ![]() region
region ![]() .
The one-dimensional segregation problem fullfils the following initial and interface conditions,
.
The one-dimensional segregation problem fullfils the following initial and interface conditions,
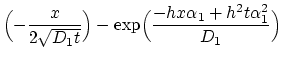 erfc
erfc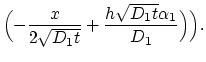
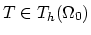
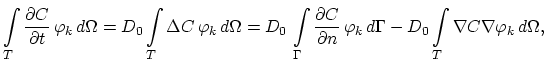 erfc
erfc