
The terms comprising a Neumann series contain high-dimensional integrals which can be efficiently calculated using stochastic sampling by Monte Carlo techniques.
Consider an integral

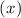 = 1 and ψ
= 1 and ψ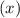 =
= 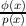 . The integral I corresponds to the mean value of ψ
. The integral I corresponds to the mean value of ψ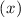 .
.
The choice of the distribution p determines various qualities of the Monte Carlo algorithm [106], namely the computational efficiency, the convergence rate and the associated trade-off with reliability (variance in the result). Often physical considerations are used to choose the distribution p.
Consider the random variables X and Ψ![[X ]](html_diss_c169x.png) : A sequence of N numbers
: A sequence of N numbers 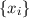 is generated according to p and is used to sample Ψ
is generated according to p and is used to sample Ψ![[X ]](html_diss_c171x.png) , thereby approximating the
mean value by an expected value:
, thereby approximating the
mean value by an expected value:
![N
I ≈ E [Ψ [X ]] =-1 ∑ ψ (x) . (3.24)
N i=1 i](html_diss_c172x.png)
This establishes the link between the Neumann series and the Monte Carlo algorithm, which will be discussed in Section 3.7.