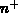 -type gate is doped by the
deposition from POCl
-type gate is doped by the
deposition from POCl source and subsequent diffusion. Similarly, in the
old PMOS technologies,
source and subsequent diffusion. Similarly, in the
old PMOS technologies, 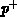 -type gate has been doped by diffusion from
BCl
-type gate has been doped by diffusion from
BCl or BBr
or BBr . The gates produced by these diffusion processes are doped
heavily with a chemical concentration as high as
. The gates produced by these diffusion processes are doped
heavily with a chemical concentration as high as 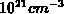 .
.




 -channel and
-channel and 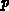 -channel. We
assume the more common
-channel. We
assume the more common 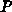 -channel MOSFETs
become buried-channel devices.
-channel MOSFETs
become buried-channel devices.