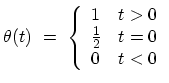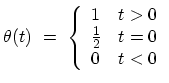- ... gets2.1
- We consider
only the valence
 and the conduction
and the conduction  energy band of
graphene and CNTs.
energy band of
graphene and CNTs.
- ... energy2.2
- Experimentally the value
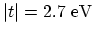 has been reported [19].
has been reported [19].
- ... systems2.3
- A mesoscopic system is a solid small enough in size,
so that the interference of electron wave-functions can be observed. A typical
size of a mesoscopic system is around
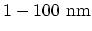 which is larger than
the microscopic size of around
which is larger than
the microscopic size of around 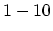 Å and smaller than the
macroscopic size which is more than
Å and smaller than the
macroscopic size which is more than
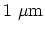 [60].
[60].
- ...
CNTs2.4
- The work function is defined as the sum of the CNT
electron affinity and half of the band-gap in the bulk.
- ... shift2.5
-
Note that this is unique for the contact between a metal and a CNT.
In a conventional, planar semiconductor device the position of the FERMI
energy is pinned by metal-induced gap states [72].
- ... state3.1
- Here the PAULI exclusion
principle which leads to a nonlinear master equation is neglected
- ... commutationA.1
- The commutation relation for
Bosons is defined by
![$ [A,B]_{-}=[A,B]=AB-BA$](img1064.png) .
.
- ... anti-commutationA.2
- The
anti-commutation relation for FERMIons is defined by
![$ [A,B]_{+}=\{A,B\}=AB+BA$](img1065.png) .
.
- ... functionB.1
- The step function
is defined as
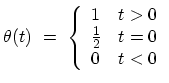
- ... functionF.1
- Screening is defined by
the inverse dielectric function. An external potential induces a charge density in
the system. This induced charge density gives rise to a change in the potential
via the COULOMB interaction, which in turn yields an induced charge density and
so forth. The result of this infinite series of charge redistribution process
is the screening of the external potential.