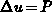 ,
, 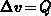 . In the
computational domain, the corresponding transformed
equations (3.3-18) - (3.3-19) have to be
solved.
. In the
computational domain, the corresponding transformed
equations (3.3-18) - (3.3-19) have to be
solved.




Elliptic methods are based on the solution of the boundary value problem
[Hil88a] 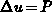 ,
, 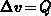 . In the
computational domain, the corresponding transformed
equations (3.3-18) - (3.3-19) have to be
solved.
. In the
computational domain, the corresponding transformed
equations (3.3-18) - (3.3-19) have to be
solved.
This system of nonlinear elliptic PDEs is discretized on the geometric grid using nine-point finite differences. The resulting system of coupled nonlinear algebraic equations is solved with a nonlinear SOR Algorithm [Ort70].
A superimposed iteration scheme (3.3-21) - (3.3-23)
determines the source functions 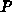 and
and 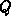 at the boundaries which are used to
avoid clustering of gridlines at concave corners, and to allow orthogonality
control at the boundaries [Hil88a], [Bau90].
at the boundaries which are used to
avoid clustering of gridlines at concave corners, and to allow orthogonality
control at the boundaries [Hil88a], [Bau90].
Here 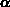 denotes the angle of intersection of gridlines (3.3-24)
(which should be equal to the required value
denotes the angle of intersection of gridlines (3.3-24)
(which should be equal to the required value 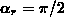 ), and
), and 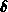 resembles the grid spacing (3.3-25).
resembles the grid spacing (3.3-25).
The upper signs in (3.3-22) and (3.3-23) relate to the
north boundary, the lower signs to the south boundary. For the east and west
boundaries, the correction terms for 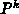 and
and 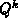 are exchanged. In the
interior,
are exchanged. In the
interior, 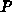 and
and 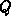 are obtained by transfinite interpolation. In his
original work [Hil88a] Hilgenstock proposed the
are obtained by transfinite interpolation. In his
original work [Hil88a] Hilgenstock proposed the 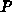 - and
- and 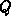 -values at
the boundary should decay exponentially into the interior of the domain.
This turned out inferior to the transfinite interpolation.
-values at
the boundary should decay exponentially into the interior of the domain.
This turned out inferior to the transfinite interpolation.